数据结构
划分树
结构
划分树是基于线段树的一种数据结构,主要用于快速求出(log(n)时间的时间复杂度内))序列区间的第K大/小值
划分树主要分为两部分:建树和查询
建树
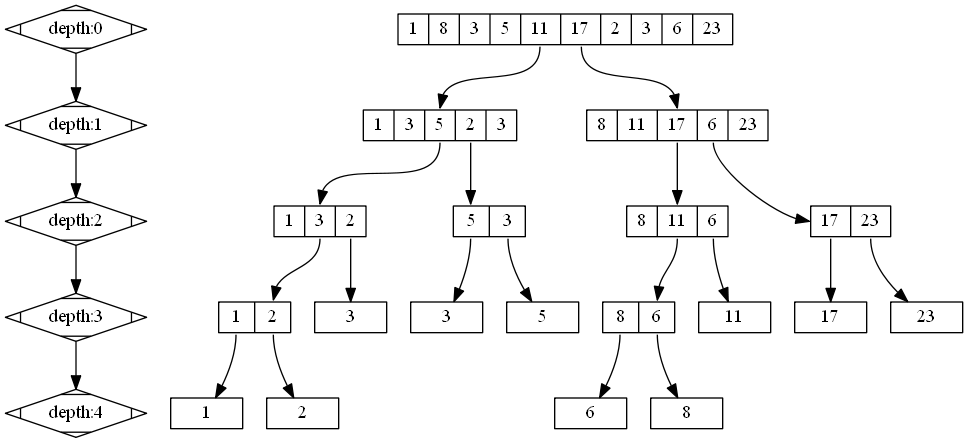
如图所示,划分树本质上是线段树加模拟快速排序.
首先我们先创建一个数组sorted[],用以保存原数组排序后的结果.和toleft[],用以记录当前节点及之前节点被分到左子树的个数(后文会详细解释)
然后树的主体我们采用tree[][]这个二维数组来实现,第一维是层,第二维是数组元素
递归建树过程,主体思想是
- 针对区间[L,R],我们根据
sorted[(L+R)/2]来将这个数组一分为二,将小的放到左子树(即此层分裂后下一层的左侧的区间),大的放到右侧. - 然后更改一下toleft数组,记录当前节点及之前节点被分到左子树的个数
- 向左右子树递归,当区间长度为1时终止
但是上文的操作会带来一个问题,就是如果中位数有重复的情况怎么办,其实解决方法也简单,就是手动维护让左右两个区间的个数仍然是各为一半就可以了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
const int MAXN=100010;
int tree[30][MAXN];// 表示每层每个位置的值
int sorted[MAXN];// 已经排序的数,这个是从1开始的
int toleft[30][MAXN];// toleft[p][i]表示第i层从1到i有多少个数分入左边
void build(int l,int r,int dep){ // 建树
if(l==r) // 终止条件,区间长度为1
return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
int same=mid-l+1;// same表示等于中间值而且预计要分入左边的个数
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) { // 数出多少个重复的中位数
if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid]){
same--;
}
}
int lpos=l; // 左边界
int rpos=mid+1; // 右边界
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){ // 对于每个元素都讨论是分向左边还是右边
if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid])// 比中间的数小,分入左边
tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i];
else if(tree[dep][i]==sorted[mid]&&same>0){ // 与中间数相等,此处通过讨论same,来判断左侧还需不需要填入与中位数相等的数,如果需要,就加入
tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i];
same--;
}
else // 比中间值大,分入右边
tree[dep+1][rpos++]=tree[dep][i];
toleft[dep][i]=toleft[dep][l-1]+lpos-l;// 前缀思想,记录从1到i放左边的个数
}
// 向左右子树递归
build(l,mid,dep+1);
build(mid+1,r,dep+1);
}
查询
数据结构的形式决定其使用的方法,针对这种数据结构,不难发现,其查询也一定是向下递归,逐步缩小区间,然后定位某个数为最终答案.
首先,我们先定义接口int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int dep,int k);[L,R]是大区间,[l,r]是查询小区间,dep是层次,k即”第K小”
查询时,如果查询区间长度变成1,则查询终止,目标已找到.若区间长度大于1,则最后的答案一定位于其左右孩子区间的其中一个,所以只需要向下查询即可.
至于向下查询,我们不难想到,如果其左孩子中的元素个数大于k,则答案一定在左子树中,否则一定在右子树中,这也就是向左还是向右搜索的判断条件.
注:以上二分的是大区间,但对于查询区间(小区间),仍然需要讨论
仔细思索,发现小区间在向下传递的过程中是应该发生变化的,(以向左孩子区间传递为例)因为在[l,r]区间中向左区间传递的数量是不定的,可能很多,然后l就会变小.可能很少,l就会变大,所以l,r应该根据[l,r]区间向左子树传递的个数来确定.
至于具体方法,不难发现,[L,l-1]内被分配到左子树的元素,不在查找之列,但相对位置不变,这些元素一定排在前面(因为先被加入到下一层),以此来确定左边界,其个数是toleft[l-1]-toleft[L-1],所以 newl=L+toleft[dep][l-1]-toleft[dep][L-1]
我们再对向右区间传递的情况进行讨论,我们发现,在r之前的元素,无论是分配到了左区间还是右区间,都对r的位置没有影响,但是在[r+1,R]区间中的元素如果分到的左区间,则会导致r的右移,也就是会导致r右移toleft[dep][R]-toleft[dep][r]个单位,同理新的l也可以由新的r来确定,即newl == newr - [l,r]中转移到右侧的元素个数 == newr - ([l,r]区间长度 - [l,r]中转移的左侧的元素个数),即newl = newr - (r-l-cnt)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
//查询区间第k大的数,[L,R]是大区间,[l,r]是要查询的小区间
int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int dep,int k){
if(l==r) // 区间长度为1,即终止条件
return tree[dep][l];
int mid=(L+R)>>1;
int cnt=toleft[dep][r]-toleft[dep][l-1];// [l,r]中位于左边的个数
if(cnt>=k){ // 答案在左区间
// L+要查询的区间前被放在左边的个数
int newl=L+toleft[dep][l-1]-toleft[dep][L-1];
// 左端点加上查询区间会被放在左边的个数
int newr=newl+cnt-1;
return query(L,mid,newl,newr,dep+1,k);
}
else{ // 答案在右区间
// 同理此处先确定右端点,再确定左端点
int newr=r+toleft[dep][R]-toleft[dep][r];
int newl=newr-(r-l-cnt);
return query(mid+1,R,newl,newr,dep+1,k-cnt);
}
}
使用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
// 求第k小模板性很强
/*
HDU 2665 Kth number
划分树
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=100010;
int tree[30][MAXN];//表示每层每个位置的值
int sorted[MAXN];//已经排序的数
int toleft[30][MAXN];//toleft[p][i]表示第i层从1到i有多少个数分入左边
void build(int l,int r,int dep){
if(l==r)return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
int same=mid-l+1;//表示等于中间值而且被分入左边的个数
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)
if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid])
same--;
int lpos=l;
int rpos=mid+1;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){
if(tree[dep][i]<sorted[mid])//比中间的数小,分入左边
tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i];
else if(tree[dep][i]==sorted[mid]&&same>0){
tree[dep+1][lpos++]=tree[dep][i];
same--;
}
else //比中间值大分入右边
tree[dep+1][rpos++]=tree[dep][i];
toleft[dep][i]=toleft[dep][l-1]+lpos-l;//从1到i放左边的个数
}
build(l,mid,dep+1);
build(mid+1,r,dep+1);
}
//查询区间第k大的数,[L,R]是大区间,[l,r]是要查询的小区间
int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int dep,int k){
if(l==r)return tree[dep][l];
int mid=(L+R)>>1;
int cnt=toleft[dep][r]-toleft[dep][l-1];//[l,r]中位于左边的个数
if(cnt>=k){
//L+要查询的区间前被放在左边的个数
int newl=L+toleft[dep][l-1]-toleft[dep][L-1];
//左端点加上查询区间会被放在左边的个数
int newr=newl+cnt-1;
return query(L,mid,newl,newr,dep+1,k);
}
else{
int newr=r+toleft[dep][R]-toleft[dep][r];
int newl=newr-(r-l-cnt);
return query(mid+1,R,newl,newr,dep+1,k-cnt);
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
int n,m;
int s,t,k;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));// 这个必须
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){// 从1开始
scanf("%d",&tree[0][i]);
sorted[i]=tree[0][i];
}
// 先排序sorted[]数组
sort(sorted+1,sorted+n+1);
// 然后从第0层开始初始化
build(1,n,0);
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&s,&t,&k);
// 下面函数参数中的1,n,0都是固定的,即从[1,n]的第0层开始
printf("%d\n",query(1,n,s,t,0,k));
}
}
return 0;
}
应用(未完)
我们不难发现,求区间第k大的算法就是上文的query,我们根据中学知识可得,中位数的大小就是区间里第(len+1)/2大的数
此处给出一个题,先mark一下,过几天更新答案
主席树
又叫可持久化线段树,
主席树就是利用函数式编程的思想来使线段树支持询问历史版本、同时充分利用它们之间的共同数据来减少时间和空间消耗的增强版的线段树。
此处mark一下,之后补充
伸展树(Splay tree)
[<算法合集之伸展树的基本操作和应用>](https://max.book118.com/html/2017/0810/127135517.shtm)
伸展树是一种自平衡二叉搜索树,其特点是通过旋转来获得较好的平摊时间复杂度,也就是未必保证每一次的操作都是O(lg N),但是连续m次的均摊复杂度不大于O(M*lg N),而且不像AVL一样需要额外的空间来记录树的平衡状况,其操作也比红黑树要简单,编码难度低,因此在竞赛中经常使用
伸展树常用的操作有 插入,查询,删除,求最大值,最小值,求前驱,求后继,合并,分离
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
// kuangbin 的模板
#define MAXN 2000000
int ch[MAXN][2], fa[MAXN], data[MAXN];
int root, tot;
void splaInit(){ // 初始化
root = 0;
tot = 0;
}
void newNode(int &x, int k, int father) { // 新建节点,在创建根节点时只能采取这个方式构造: newNode(root,a,0)
x = ++tot;
ch[x][0] = ch[x][1] = 0;
data[x] = k;
fa[x] = father;
}
void rotate(int x, int kind) { //kind = 0 ,左旋,kind = 1 ,右旋
int y = fa[x];
ch[y][!kind] = ch[x][kind];
fa[ch[x][kind]] = y;
if (fa[y])ch[fa[y]][ch[fa[y]][1] == y] = x;
fa[x] = fa[y];
ch[x][kind] = y;
fa[y] = x;
}
void Splay(int x, int goal) { //将节点x转到节点goal下面
while (fa[x] != goal) {
if (fa[fa[x]] == goal)rotate(x, ch[fa[x]][0] == x);
else {
int y = fa[x];
int z = fa[y];
int kind = (ch[z][0] == y);
if (ch[y][kind] == x) {
rotate(x, !kind);
rotate(x, kind);
} else {
rotate(y, kind);
rotate(x, kind);
}
}
}
if (goal == 0) // 此时根节点已经发生了变化,变成了x
root = x;
}
int insert(int k) { // 向伸展树中插入元素
int r = root;
while (ch[r][data[r] < k]) {
if (data[r] == k) {//避免重复插入
Splay(r, 0);
return 0;
}
r = ch[r][data[r] < k];
}
newNode(ch[r][data[r] < k], k, r);
Splay(ch[r][data[r] < k], 0);
return 1;
}
// 本质是求左子树的最大值
int get_pree(int k) { // 寻找前驱(实际上返回的是前驱节点在data数组中的下标),若无前驱,则返回-1
int d = ch[k][0];
if (d == 0)
return -1;//没有前驱
while (ch[d][1]) {
d = ch[d][1];
}
return d;
}
// 本质是求右子树的最小值
int get_next(int k) { // 寻找后继(实际上返回的是前驱节点在data数组中的下标),若无后继,则返回-1
int d = ch[k][1];
if (d == 0)
return -1;//没有后继
while (ch[d][0]) {
d = ch[d][0];
}
return d;
}
int main(){
splaInit();
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
int tmp;
cin>>tmp;
if(i){
insert(tmp); // 此处可通过insert函数的返回值来判断是否插入成功(插入不成功的情况是已经存在与之相同大小的元素)
}else{
newNode(root,tmp,0);
}
}
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
// Clove_unique 的模板,正确性稍后验证
// 然而这个版本有一点点问题,在于其求前驱和后继的方法不太方便而且插入并不返回正确与否,所以决定进行修改,与kuangbin 的进行结合
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000000
int ch[MAXN][2],f[MAXN],size[MAXN],cnt[MAXN],key[MAXN];
int sz,root;
inline void clear(int x){
ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=f[x]=size[x]=cnt[x]=key[x]=0;
}
inline bool get(int x){
return ch[f[x]][1]==x;
}
inline void update(int x){
if (x){
size[x]=cnt[x];
if (ch[x][0]) size[x]+=size[ch[x][0]];
if (ch[x][1]) size[x]+=size[ch[x][1]];
}
}
inline void rotate(int x){
int old=f[x],oldf=f[old],whichx=get(x);
ch[old][whichx]=ch[x][whichx^1]; f[ch[old][whichx]]=old;
ch[x][whichx^1]=old; f[old]=x;
f[x]=oldf;
if (oldf)
ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1]==old]=x;
update(old); update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x){
for (int fa;fa=f[x],f[x];rotate(x))
if (f[fa])
rotate((get(x)==get(fa))?fa:x);
root=x;
}
inline void insert(int x){
if (root==0){sz++; ch[sz][0]=ch[sz][1]=f[sz]=0; root=sz; size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1; key[sz]=x; return;}
int now=root,fa=0;
while(1){
if (x==key[now]){
cnt[now]++; update(now); update(fa); splay(now); break;
}
fa=now;
now=ch[now][key[now]<x];
if (now==0){
sz++;
ch[sz][0]=ch[sz][1]=0;
f[sz]=fa;
size[sz]=cnt[sz]=1;
ch[fa][key[fa]<x]=sz;
key[sz]=x;
update(fa);
splay(sz);
break;
}
}
}
inline int find(int x){
int now=root,ans=0;
while(1){
if (x<key[now])
now=ch[now][0];
else{
ans+=(ch[now][0]?size[ch[now][0]]:0);
if (x==key[now]){
splay(now); return ans+1;
}
ans+=cnt[now];
now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int findx(int x){
int now=root;
while(1){
if (ch[now][0]&&x<=size[ch[now][0]])
now=ch[now][0];
else{
int temp=(ch[now][0]?size[ch[now][0]]:0)+cnt[now];
if (x<=temp) return key[now];
x-=temp; now=ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int pre(){
int now=ch[root][0];
while (ch[now][1]) now=ch[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int next(){
int now=ch[root][1];
while (ch[now][0]) now=ch[now][0];
return now;
}
inline void del(int x){
int whatever=find(x);
if (cnt[root]>1){cnt[root]--; update(root); return;}
if (!ch[root][0]&&!ch[root][1]) {clear(root); root=0; return;}
if (!ch[root][0]){
int oldroot=root; root=ch[root][1]; f[root]=0; clear(oldroot); return;
}
else if (!ch[root][1]){
int oldroot=root; root=ch[root][0]; f[root]=0; clear(oldroot); return;
}
int leftbig=pre(),oldroot=root;
splay(leftbig);
ch[root][1]=ch[oldroot][1];
f[ch[oldroot][1]]=root;
clear(oldroot);
update(root);
}
int main(){
int n,opt,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;++i){
scanf("%d%d",&opt,&x);
switch(opt){
case 1: insert(x); break;
case 2: del(x); break;
case 3: printf("%d\n",find(x)); break;
case 4: printf("%d\n",findx(x)); break;
case 5: insert(x); printf("%d\n",key[pre()]); del(x); break;
case 6: insert(x); printf("%d\n",key[next()]); del(x); break;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
// 经过改进与融合,我们得到了如下版本(kuangbin + Clove_unique)的版本,支持插入(可根据返回值判断是否插入成功),删除,寻找前驱,寻找后继,根据值查询名次,和根据名次查询值,且AC了BZOJ的模板题(普通二叉树)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 1000000
int ch[MAXN][2], f[MAXN], size[MAXN], cnt[MAXN], data[MAXN];
int tot, root;
int abs(int x) {
if (x >= 0)
return x;
return -x;
}
inline void clear(int x) {
ch[x][0] = ch[x][1] = f[x] = size[x] = cnt[x] = data[x] = 0;
}
inline bool get(int x) {
return ch[f[x]][1] == x;
}
inline void update(int x) {
if (x) {
size[x] = cnt[x];
if (ch[x][0]) size[x] += size[ch[x][0]];
if (ch[x][1]) size[x] += size[ch[x][1]];
}
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int old = f[x], oldf = f[old], whichx = get(x);
ch[old][whichx] = ch[x][whichx ^ 1];
f[ch[old][whichx]] = old;
ch[x][whichx ^ 1] = old;
f[old] = x;
f[x] = oldf;
if (oldf)
ch[oldf][ch[oldf][1] == old] = x;
update(old);
update(x);
}
inline void splay(int x) {
for (int fa; fa = f[x], f[x]; rotate(x))
if (f[fa])
rotate((get(x) == get(fa)) ? fa : x);
root = x;
}
inline int insert(int x) {
if (root == 0) {
tot++;
ch[tot][0] = ch[tot][1] = f[tot] = 0;
root = tot;
size[tot] = cnt[tot] = 1;
data[tot] = x;
return 1;
}
int now = root, fa = 0;
while (1) {
if (x == data[now]) {
cnt[now]++;
update(now);
update(fa);
splay(now);
return 0;
}
fa = now;
now = ch[now][data[now] < x];
if (now == 0) {
tot++;
ch[tot][0] = ch[tot][1] = 0;
f[tot] = fa;
size[tot] = cnt[tot] = 1;
ch[fa][data[fa] < x] = tot;
data[tot] = x;
update(fa);
splay(tot);
return 1;
}
}
}
inline int find(int x) {
int now = root, ans = 0;
while (1) {
if (x < data[now])
now = ch[now][0];
else {
ans += (ch[now][0] ? size[ch[now][0]] : 0);
if (x == data[now]) {
splay(now);
return ans + 1;
}
ans += cnt[now];
now = ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int findx(int x) {
int now = root;
while (1) {
if (ch[now][0] && x <= size[ch[now][0]])
now = ch[now][0];
else {
int temp = (ch[now][0] ? size[ch[now][0]] : 0) + cnt[now];
if (x <= temp) return data[now];
x -= temp;
now = ch[now][1];
}
}
}
inline int pre() {
int now = ch[root][0];
while (ch[now][1]) now = ch[now][1];
return now;
}
inline int next() {
int now = ch[root][1];
while (ch[now][0]) now = ch[now][0];
return now;
}
int get_pree(int k) {
int d = ch[k][0];
if (d == 0)
return -1;//没有前驱
while (ch[d][1]) {
d = ch[d][1];
}
return d;
}
int get_next(int k) {
int d = ch[k][1];
if (d == 0)
return -1;//没有后继
while (ch[d][0]) {
d = ch[d][0];
}
return d;
}
inline void del(int x) {
int whatever = find(x);
if (cnt[root] > 1) {
cnt[root]--;
update(root);
return;
}
if (!ch[root][0] && !ch[root][1]) {
clear(root);
root = 0;
return;
}
if (!ch[root][0]) {
int oldroot = root;
root = ch[root][1];
f[root] = 0;
clear(oldroot);
return;
} else if (!ch[root][1]) {
int oldroot = root;
root = ch[root][0];
f[root] = 0;
clear(oldroot);
return;
}
int leftbig = pre(), oldroot = root;
splay(leftbig);
ch[root][1] = ch[oldroot][1];
f[ch[oldroot][1]] = root;
clear(oldroot);
update(root);
}
int main() {
int n, opt, x;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
cin >> opt >> x;
switch (opt) {
case 1:
insert(x);
break;
case 2:
del(x);
break;
case 3:
cout << find(x) << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << findx(x) << endl;
break;
case 5:
insert(x);
cout << data[get_pree(root)] << endl;
del(x);
break;
case 6:
insert(x);
cout << data[get_next(root)] << endl;
del(x);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}